Join the AI Workshop to learn more about AI and how it can be applied to web development. Next cohort February 1st, 2026
The AI-first Web Development BOOTCAMP cohort starts February 24th, 2026. 10 weeks of intensive training and hands-on projects.
uniq is a command useful to sort lines of text.
You can get those lines from a file, or using pipes from the output of another command:
uniq dogs.txt
ls | uniqYou need to consider this key thing: uniq will only detect adjacent duplicate lines.
This implies that you will most likely use it along with sort:
sort dogs.txt | uniqThe sort command has its own way to remove duplicates with the -u (unique) option. But uniq has more power.
By default it removes duplicate lines:
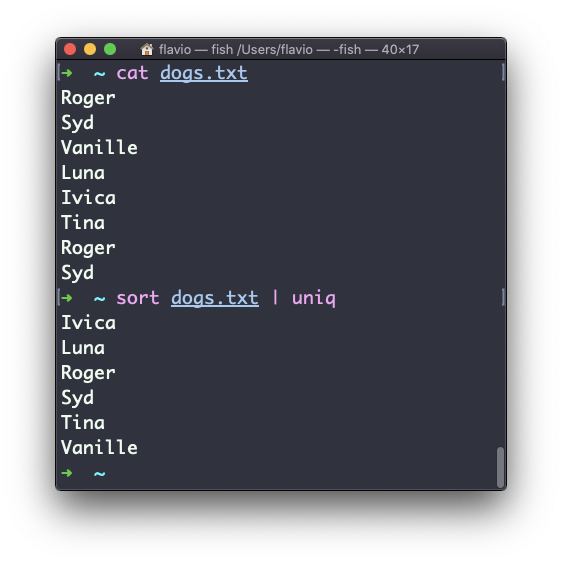
You can tell it to only display duplicate lines, for example, with the -d option:
sort dogs.txt | uniq -d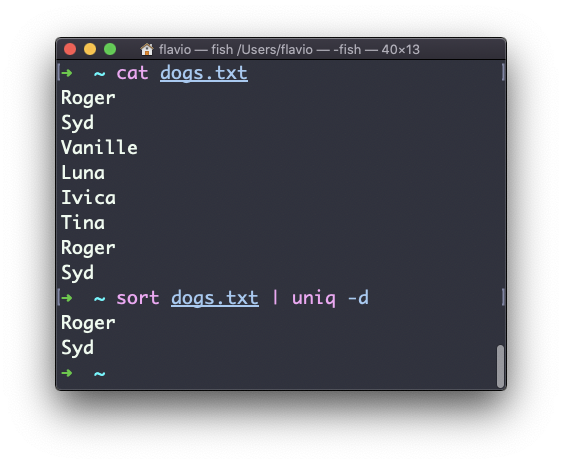
You can use the -u option to only display non-duplicate lines:
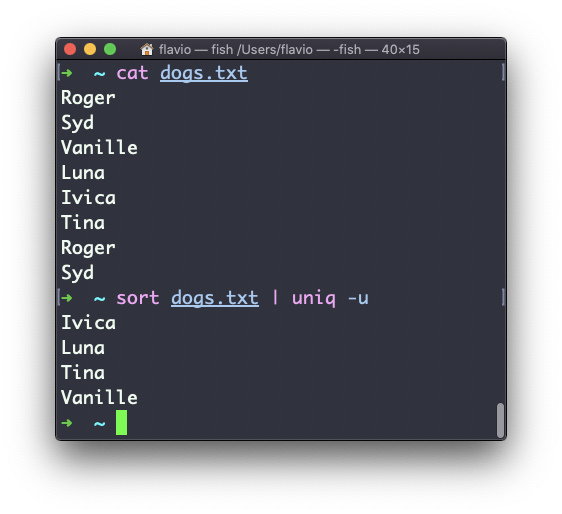
You can count the occurrences of each line with the -c option:
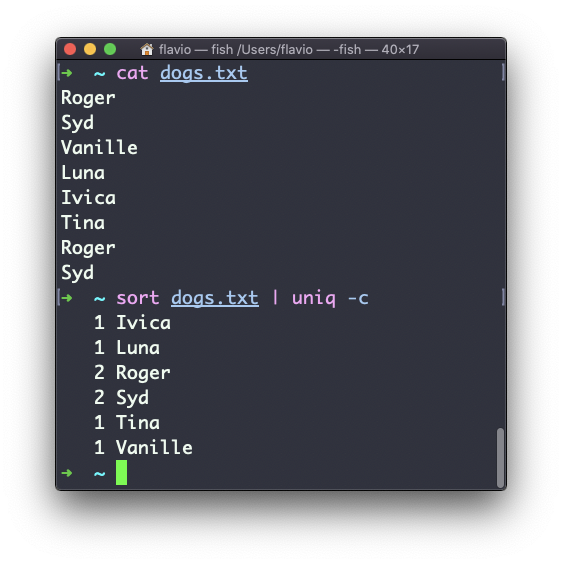
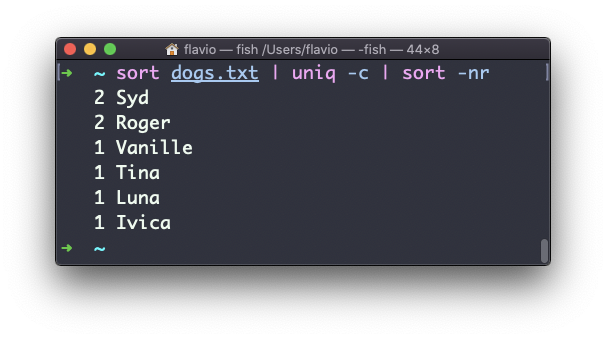
Use the special combination:
sort dogs.txt | uniq -c | sort -nrto then sort those lines by most frequent:
The uniq command works on Linux, macOS, WSL, and anywhere you have a UNIX environment
Lessons in this unit:
| 0: | Introduction |
| 1: | grep - Search Text |
| 2: | find - Search Files |
| 3: | sort - Sort Lines |
| 4: | ▶︎ uniq - Remove Duplicates |
| 5: | diff - Compare Files |
| 6: | wc - Word Count |
| 7: | xargs - Build Command Lines |