Creating commands
We’ve used Artisan, the Laravel command line tool, to perform various actions:
-
php artisan serve -
php artisan make:migration -
php artisan migrate -
php artisan make:model -
php artisan make:controller -
php artisan breeze:install
Those are all built-in commands.
There are many, many more.
Some you’ll use often, some you’ll never use.
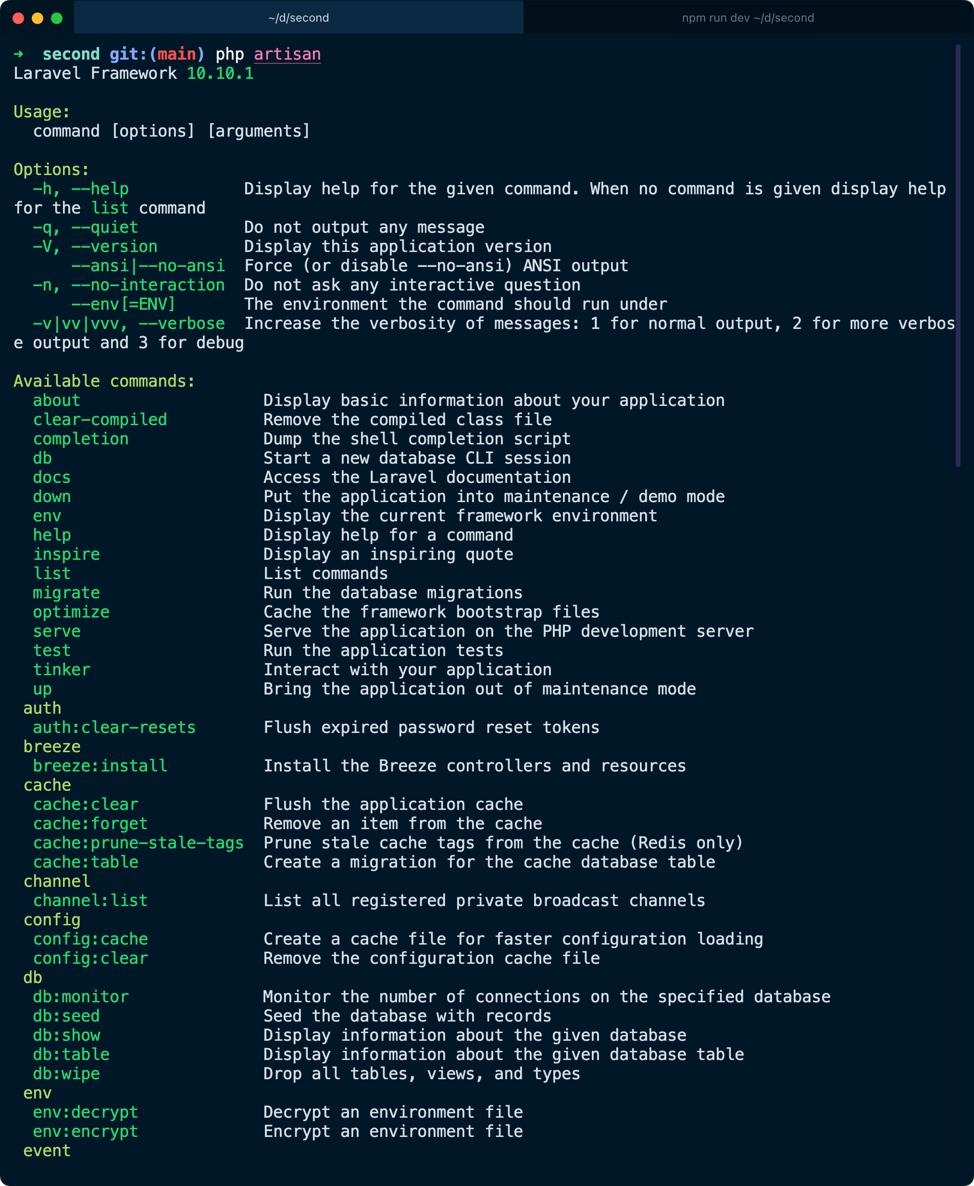
Run php artisan to see them all with a short explanation:
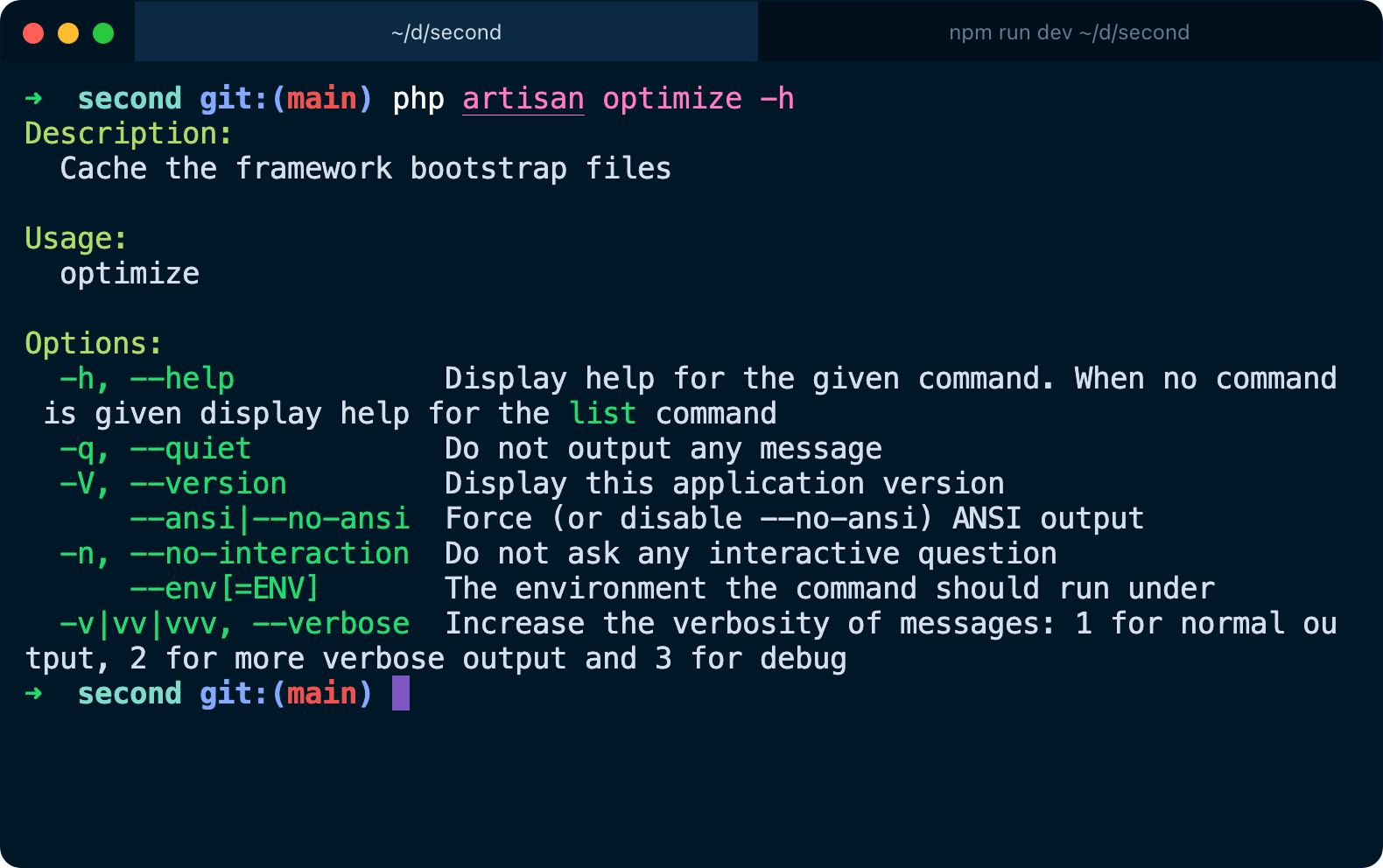
And to see how to use a command in particular, run php artisan -h:
You can create your own commands, too.
Run
php artisan make:command MyCommand
This creates a file in app/Console/Commands/MyCommand.php pre-filled with some code:
<?php
namespace App\Console\Commands;
use Illuminate\Console\Command;
class MyCommand extends Command
{
/**
* The name and signature of the console command.
*
* @var string
*/
protected $signature = 'app:my-command';
/**
* The console command description.
*
* @var string
*/
protected $description = 'Command description';
/**
* Execute the console command.
*/
public function handle()
{
//
}
}
$signature defines how the command will be called, in this case you can run
it using
php artisan app:my-command
In the handle() method you’ll write the code that runs when the command
is executed.
public function handle()
{
//
}
The simplest code could be printing something to the console, for example:
public function handle()
{
$this->info('test!');
}
Now try running php artisan app:my-command:

You can do lots of things in a command. You can accept arguments, interactively ask something to the user using prompts to confirm or asking for input, or let them choose between different options, you can format output in different ways…
Commands are great to perform one-off tasks, maintenance, and much more. Inside a command you have access to all the goodies provided by Laravel, including your own code, classes, and more.
You can also call other commands. And commands can be ran by any part of your Laravel app.
You can also schedule commands using schedules. The server can be configured to run Laravel’s schedules, and then any schedule configured in Laravel will be executed as needed.