Join the AI Workshop to learn more about AI and how it can be applied to web development. Next cohort February 1st, 2026
The AI-first Web Development BOOTCAMP cohort starts February 24th, 2026. 10 weeks of intensive training and hands-on projects.
Now this is a very simple example.
But I want to introduce validation now, because it’s a super important topic and it’s a feature built into the browser.
The most basic form of validation is to set a field as mandatory using the required attribute:
<form method='post'>
<input type='text' name='city' required />
</form>If you try sending the form with an empty input, the browser will raise a validation error, telling you to fill the field:
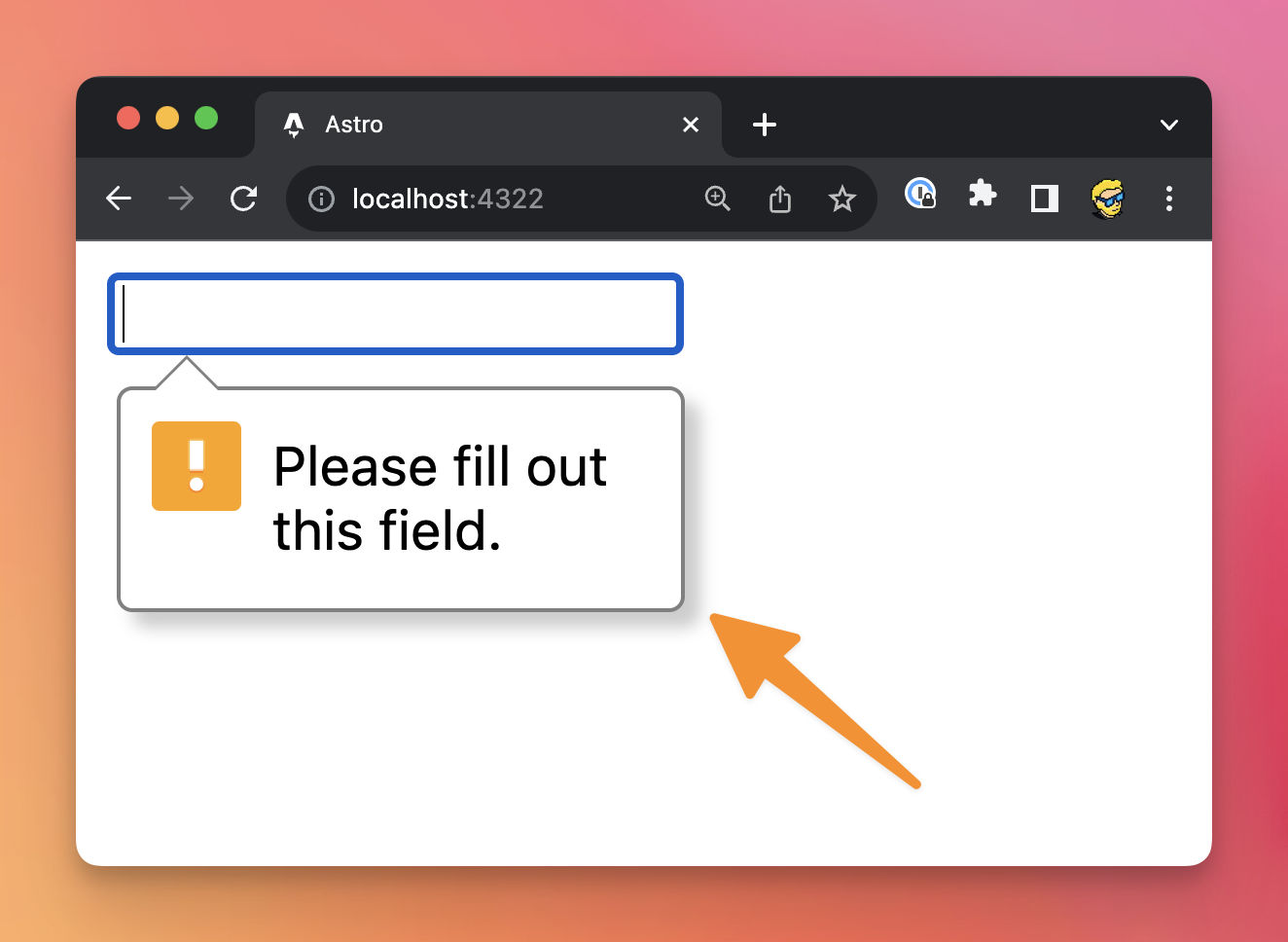
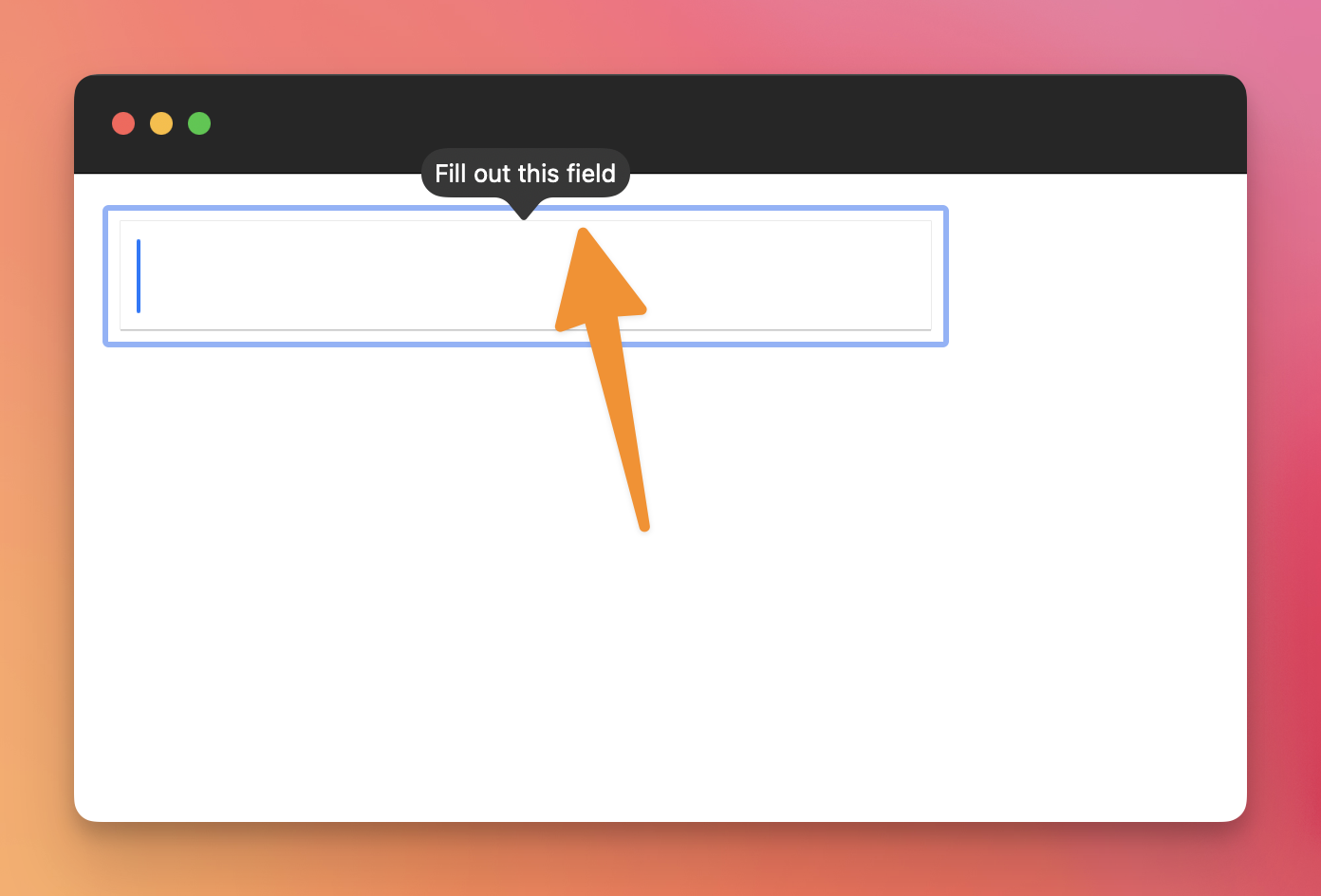
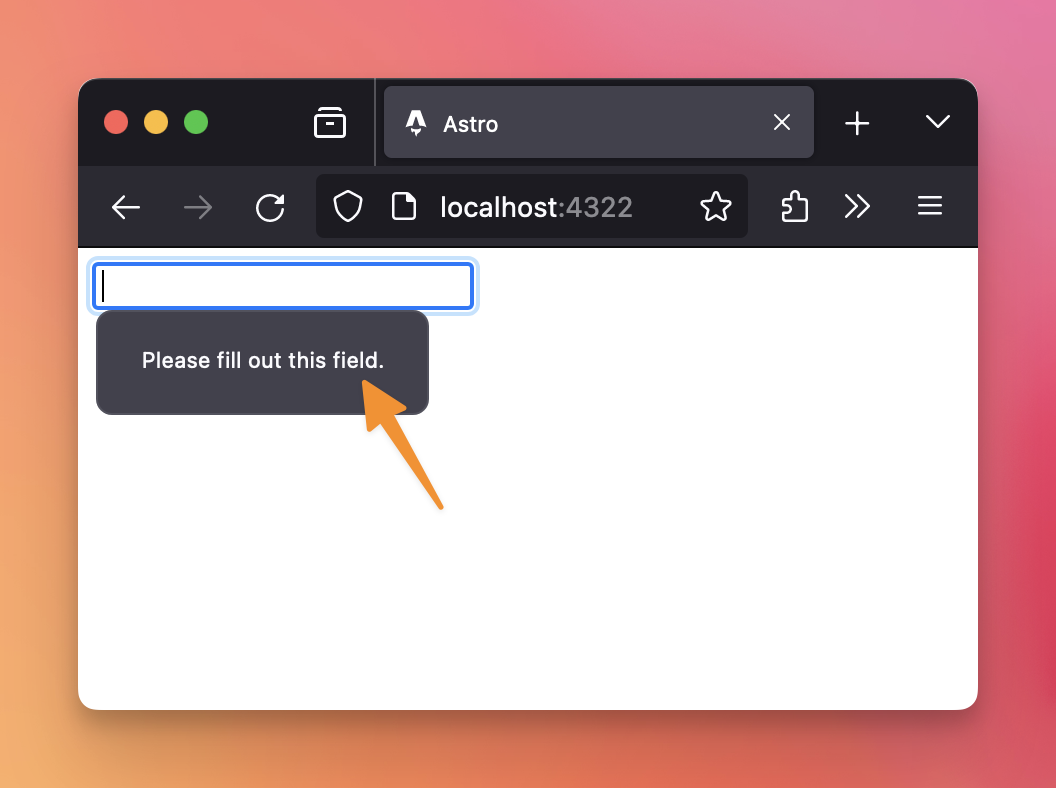
As you can see, the exact appearance of this error varies depending on the browser used (note: you can customize it, if you want).
We can use other attributes to do other kinds of validation for text input fields: minlength to set a minimum length of the string entered, maxlength to set a maximum length of the string entered. And pattern to specify a regular expression that will be used to validate the data (something a bit more advanced, but possible).
It’s important to note that this is client-side validation. You still need to validate data on the server, and return an error message if some data in the form is not valid.
Lessons in this unit:
| 0: | Introduction |
| 1: | Creating a form |
| 2: | Submitting a form |
| 3: | Receiving the form data |
| 4: | ▶︎ Form validation |
| 5: | More tags useful in forms |
| 6: | Disabled form fields are not POSTed |