Join the AI Workshop to learn more about AI and how it can be applied to web development. Next cohort February 1st, 2026
The AI-first Web Development BOOTCAMP cohort starts February 24th, 2026. 10 weeks of intensive training and hands-on projects.
You create a form using the <form> HTML tag:
<form>
</form>Inside this form you’ll have form fields, and a button to submit the form.
The simplest form field is a text input, which you create using the input tag:
<form>
<input name="city" />
</form>Typically an input element as a type attribute, because you can create many different kinds of inputs, as we’ll see in the unit dedicated to form fields. type="text" is the default for input fields, so you can omit it, but it’s nice to set it:
<form>
<input type="text" name="city" />
</form>You can test it by creating a simple index.html file with this content:
<html lang='en'>
<head>
<title>Form example</title>
</head>
<body>
<form>
<input type='text' name='city' />
</form>
</body>
</html>and opening it with the browser from your filesystem.
This is how the browser renders a form with an input field by default:
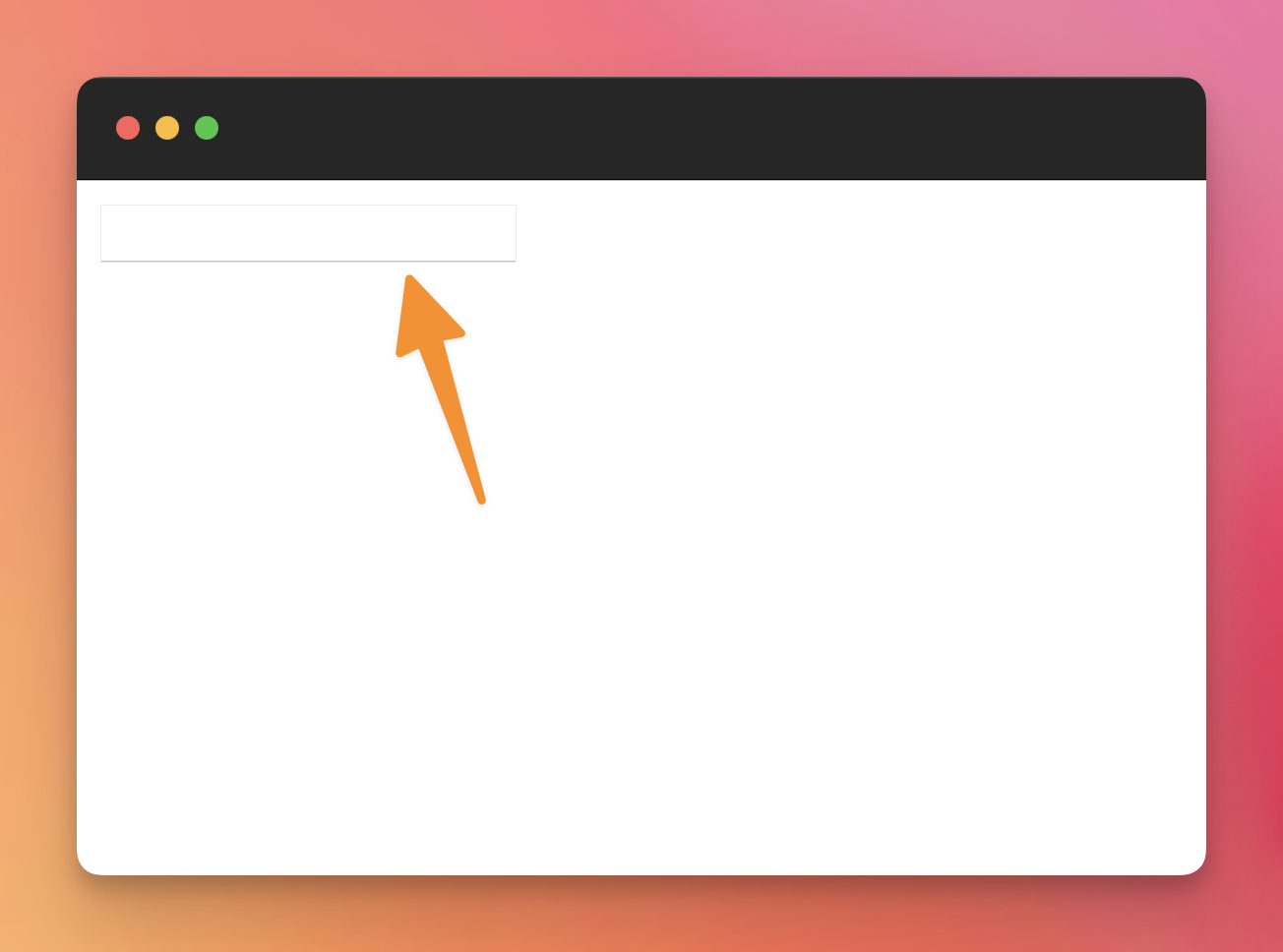
If you click the item, or press the tab key on your keyboard, the form will enter in a “focused” state, and the browser will add some visual cues to show that:
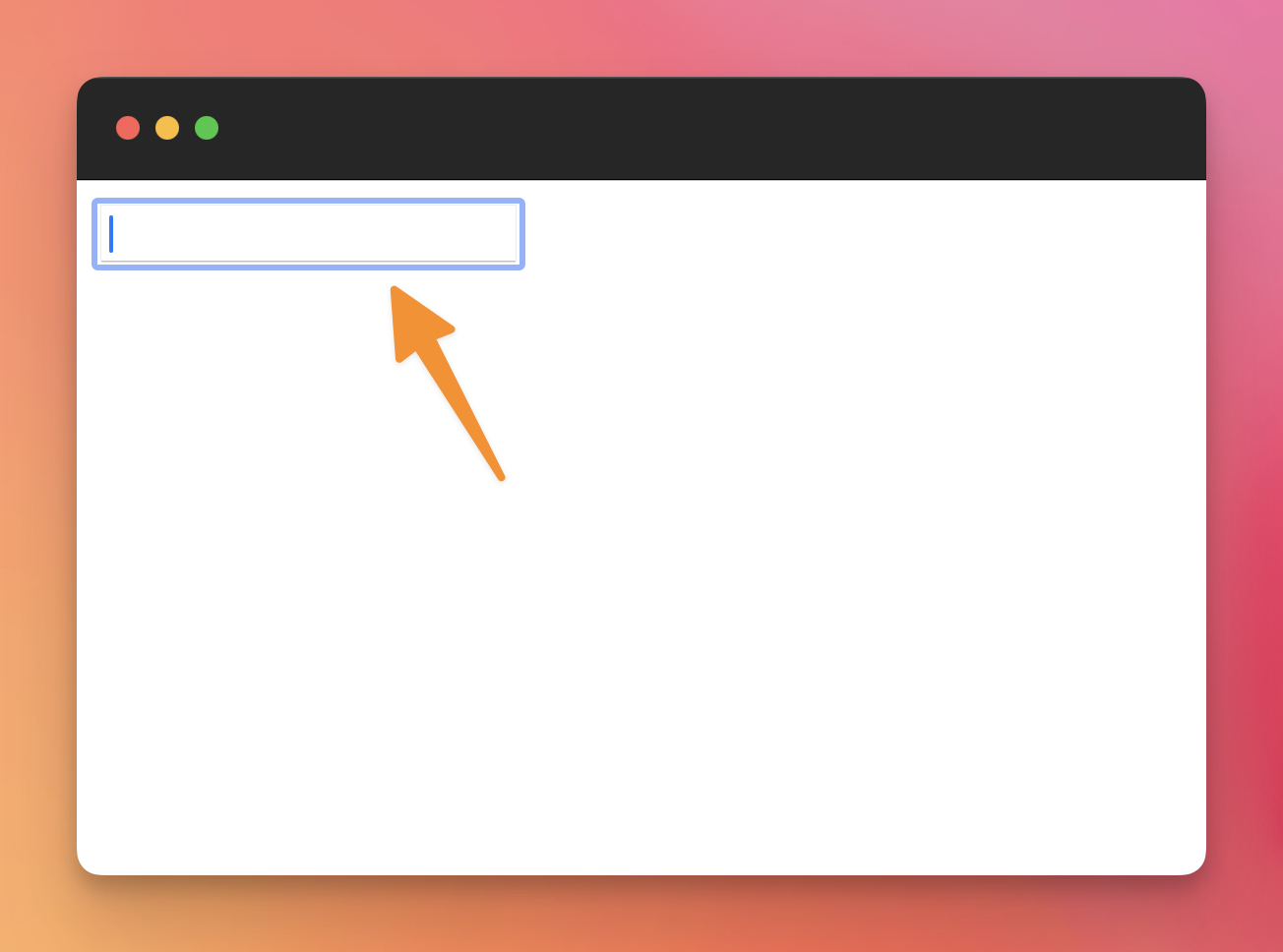
Now we can write in the field:
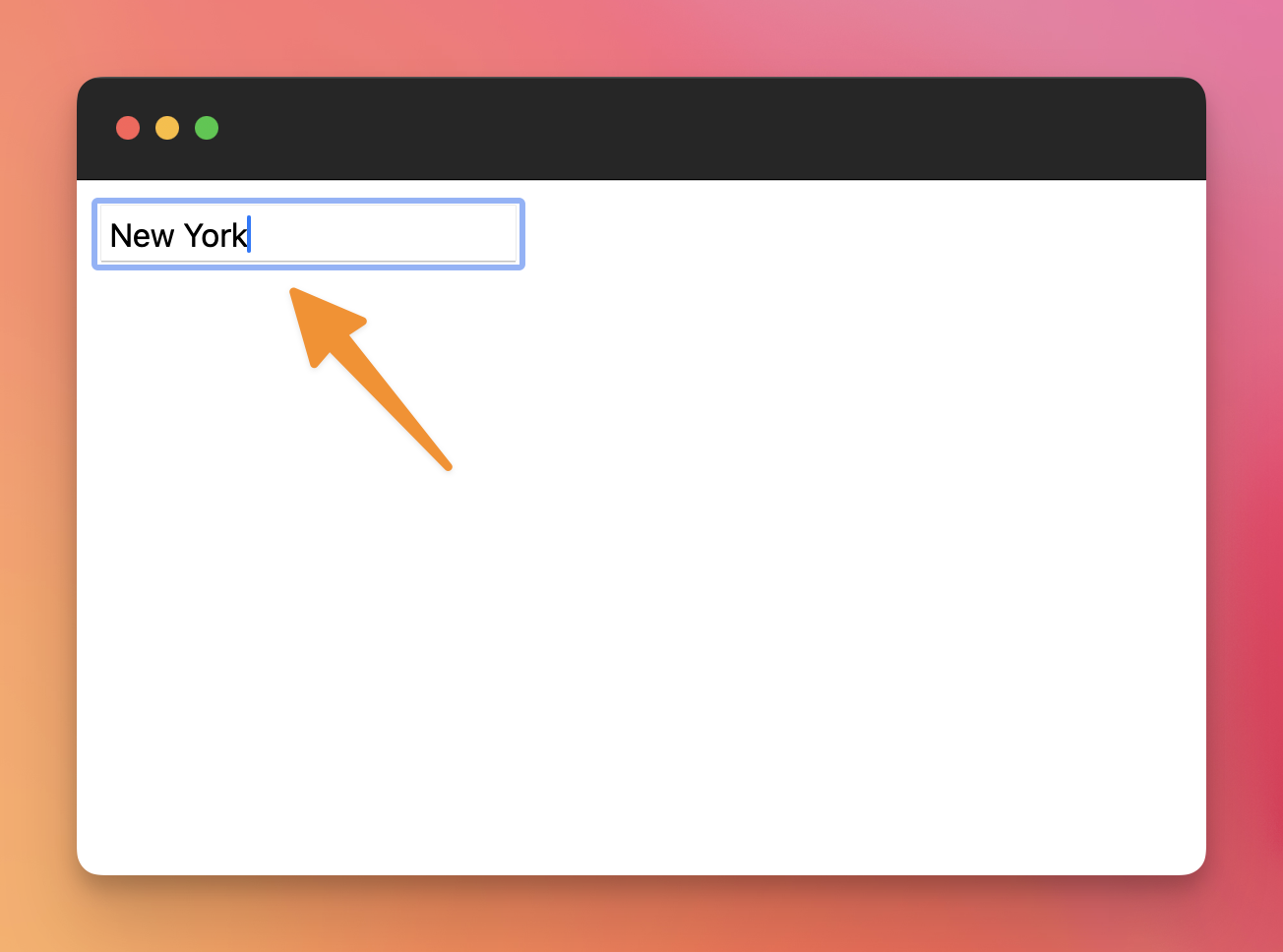
The data we write will be sent somewhere when you submit the form.
Lessons in this unit:
| 0: | Introduction |
| 1: | ▶︎ Creating a form |
| 2: | Submitting a form |
| 3: | Receiving the form data |
| 4: | Form validation |
| 5: | More tags useful in forms |
| 6: | Disabled form fields are not POSTed |